The main components and materials of a lithium-ion battery
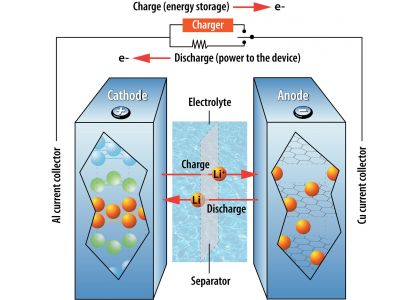
Here are the main components and materials of a lithium-ion battery:
- Anode: The anode is the negative electrode of the battery. It is typically made of graphite, which is a good conductor of electricity. The anode stores lithium ions when the battery is charging.
- Cathode: The cathode is the positive electrode of the battery. It is typically made of a lithium compound, such as lithium cobalt oxide or lithium iron phosphate. The cathode releases lithium ions when the battery is discharging.
- Electrolyte: The electrolyte is a liquid or gel that allows lithium ions to move between the anode and cathode. The electrolyte is typically made of a mixture of organic solvents and lithium salts.
- Separator: The separator is a thin film that separates the anode and cathode. It prevents the electrodes from touching each other, which would cause a short circuit. The separator is typically made of a polymer film.
- Package: The package is the outer casing of the battery. It protects the battery from damage and helps to keep the electrolyte in place. The package is typically made of plastic or metal.
In addition to these main components, lithium-ion batteries also contain a number of other materials, such as binders, conductive additives, and corrosion inhibitors. These materials help to improve the performance and durability of the battery.
Here is a table of the most common materials used in lithium-ion batteries:
|
Component
|
Material
|
|
Anode
|
Graphite, silicon, tin
|
|
Cathode
|
Lithium cobalt oxide, lithium iron phosphate, lithium manganese oxide
|
|
Electrolyte
|
Organic solvents, lithium salts
|
|
Separator
|
Polymer film
|
|
Package
|
Plastic, metal
|
